Advertisement
In Python, turning a string into an integer is a common task. While the built-in int() function is often enough, different scenarios call for different techniques. Whether you're handling formatted strings, numbers from files, or batch conversions, Python offers several methods that cover just about every situation. Some are more flexible, others are more secure. Here's a look at the main ways to handle string-to-int conversion, depending on what you're working with.
If the string contains a decimal, int() alone will cause an error. But if your goal is to extract the whole number part, passing the string through float() first solves the issue:
python
CopyEdit
s = "42.7"
num = int(float(s)) # 42
This drops everything after the decimal. It doesn’t round—so "99.9" becomes 99, not 100.
This works well when you're handling strings that might contain decimal values, but your goal is to work with integers. It’s useful in data parsing or when converting numbers from input forms that don’t restrict decimal input.
Python’s ast module includes a function called literal_eval() that safely evaluates a string containing a Python literal and returns its actual value. For converting strings like "123" into an integer, it works without a problem:
python
CopyEdit
import ast
s = "123"
num = ast.literal_eval(s)
This isn’t limited to integers. It can handle floats, booleans, lists, dictionaries—basically any valid literal that Python understands. Unlike eval(), it won’t run arbitrary code, so it’s safer for use on strings that come from external sources or saved configurations.
However, it's not designed for custom formats or loose syntax. Any deviation from Python’s literal rules will raise a ValueError or SyntaxError.
If your string data originates from JSON, json.loads() offers a clean and safe way to convert it into a number:
python
CopyEdit
import json
s = "300"
num = json.loads(s) # 300
This works perfectly if the number is a valid JSON numeric string. But JSON has stricter rules than Python’s int() function. For example, JSON doesn’t allow leading zeros:
python
CopyEdit
s = "0123"
num = json.loads(s) # Raises JSONDecodeError
So while it's accurate and dependable when working with JSON-encoded content, it’s not forgiving. Any extra characters or formatting inconsistencies will cause it to fail.

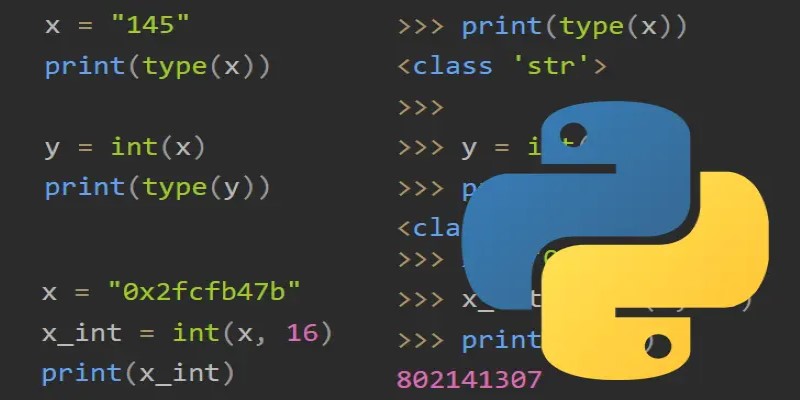
This is the standard method for turning a plain numeric string into an integer:
python
CopyEdit
s = "456"
num = int(s)
It also handles different number bases. You can convert binary, octal, or hexadecimal strings by passing the base as a second argument:
python
CopyEdit
s = "1A"
num = int(s, 16) # 26
Or:
python
CopyEdit
s = "1011"
num = int(s, 2) # 11
This method is direct and efficient, but it’s strict. Any string that includes spaces, commas, decimal points, or characters outside the expected format will raise a ValueError. It's best for clean numeric strings that you're confident won't include any unexpected extras.
eval() is capable of evaluating any Python expression stored as a string. That includes numeric values, expressions, or strings representing values in different bases:
python
CopyEdit
s = "0x10"
num = eval(s) # 16
It also handles mathematical expressions:
python
CopyEdit
s = "50 + 25"
num = eval(s) # 75
But this method comes with a clear warning. If the input isn't fully controlled or sanitized, eval() can execute dangerous code. Anything beyond your direct control—like user input or external sources—should not be passed to eval() under any circumstances. It's meant for situations where you fully trust the content and need the extra flexibility it provides.
For multiple strings, list comprehension is a clean way to apply conversion in one line:
python
CopyEdit
string_list = ["1", "2", "3"]
int_list = [int(i) for i in string_list]
This format is efficient, easy to read, and widely used when working with bulk data. If the list includes decimal numbers in string form, and you're looking to convert them to whole numbers, you can combine float() and int() directly in the comprehension:
python
CopyEdit
string_list = ["10.5", "20.1"]
int_list = [int(float(i)) for i in string_list] # [10, 20]
This keeps your code compact while handling values that aren't plain integers.
Another method for batch conversion is map(), which applies a function to every item in an iterable. If you’re converting a list of numeric strings to integers, this works just as well as list comprehension:
python
CopyEdit
string_list = ["4", "5", "6"]
int_list = list(map(int, string_list))
It’s equally valid to use a lambda if the conversion requires an extra step:
python
CopyEdit
string_list = ["7.2", "8.5"]
int_list = list(map(lambda x: int(float(x)), string_list)) # [7, 8]
map() becomes useful when the transformation is being passed as an argument to another function, or when you’re applying multiple functions in a row. It doesn’t add new capabilities over list comprehension, but it can sometimes make the structure of your code easier to manage.
Python gives you several ways to convert strings to integers. Whether you're handling plain numbers, decimals, JSON content, or batches of values, there’s a method that fits. Some are simple and direct, like int(), while others, like literal_eval() or json.loads()—offer extra structure or safety for specific contexts.
For more complex conversions, combining functions like float() and int() can help manage strings that carry decimal points. And when processing multiple strings, tools like list comprehension and map() keep your code short and clear.
Advertisement
How to use Matplotlib.pyplot.hist() in Python to create clean, customizable histograms. This guide explains bins, styles, and tips for better Python histogram plots

Learn how to convert strings to JSON objects using tools like JSON.parse(), json.loads(), JsonConvert, and more across 11 popular programming languages

Learn how AI parameters impact model performance and how to optimize them for better accuracy, efficiency, and generalization

Learn how Intel Core Ultra CPUs use advanced neural processing to unlock faster and more responsive AI experiences on PC.

Learn different methods to calculate the average of a list in Python. Whether you're new or experienced, this guide makes finding the Python list average simple and clear

Learn seven methods to convert a string to an integer in Python using int(), float(), json, eval, and batch processing tools like map() and list comprehension

Discover how Getty's Generative AI by iStock provides creators and brands with safe, high-quality commercial-use AI images.

Looking for the best AI resume builders? Check out these 10 free tools that help you craft professional resumes that stand out and get noticed by employers
Want to turn messy text into clear, structured data? This guide covers 9 practical ways to use LLMs for converting raw text into usable insights, summaries, and fields

Learn about Inception Score (IS): how it evaluates GANs and generative AI quality via image diversity, clarity, and more.

Jio Brain by Jio Platforms brings seamless AI integration to Indian enterprises by embedding intelligence into existing systems without overhauls. Discover how it simplifies real-time data use and smart decision-making
Explore effective ways for scatter plot visualization in Python using matplotlib. Learn to enhance your plots with color, size, labels, transparency, and 3D features for better data insights